[자료구조] 스택(Stack) Linked List로 구현
이번엔 스택을 연결 리스트(Linked list)로 구현해보자.
추가할 기능은 다음과 같다.
-void Push(): 스택에 아이템 추가
-void Pop(): 스택으로부터 아이템을 꺼냄
-void Top(): 스택의 맨 위의 아이템을 알려줌(observation)
-bool IsEmpty(): 스택이 모두 비었는가
-bool IsFull(): 스택이 모두 찼는가
우리는 이렇게 만들어줄 거다. topPtr은 스택의 가장 위를 가리키므로,
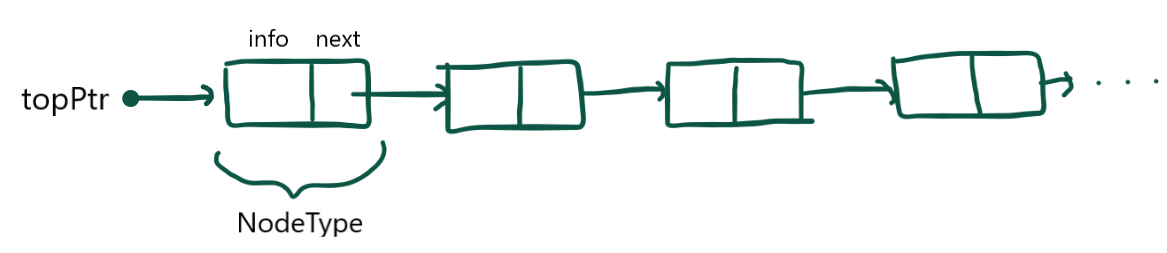
- 삽입 연산: (1)삽입 노드의 next 포인터가 탑노드를 가리키도록 연결, (2)topPtr이 삽입할 노드를 가리키도록 연결
- 삭제 연산: (1) topPtr이 다음 노드를 가리키도록 할당, (2) top 앞 메모리 해제(메모리 누수 방지)
헤더 파일을 아래와 같이 만들어준다.
//StackType.h
typedef int ItemType; //쉬운 타입 변환을 위해 선언
struct NodeType;
class FullStack{}; //예외 처리
class EmptyStack{}; //예외 처리
class StackType
{
public:
StackType();
~StackType();
bool IsFull() const;
bool IsEmpty() const;
void Push(ItemType item);
void Pop();
ItemType Top();
private:
NodeType* topPtr;
}
struct NodeType
{
ItemType info; //아이템 값을 저장
NodeType* next; //다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터
}
StackType.cpp를 만들어 안에 멤버함수의 기능을 구현해주자.
//StackType.cpp
void StackType::Push(ItemType newItem)
{
if(IsFull())
throw FullStack(); //예외 처리
else{
NodeType *location;
location = new NodeType; //삽입할 노드 생성
location->info = newItem; //생성한 노드의 info에 newItem 삽입
location->next = topPtr; //topPtr이 가리키는 노드를 가리킴
topPtr = location; //topPtr 변경
}
}
void StackType::Pop()
{
if(IsEmpty())
throw EmptyStack(); //예외 처리
else{
NodeType *tmpPtr; //노드 삭제를 위한 임시 포인터 선언
tmpPtr = topPtr; //현재 노드를 가리키는 임시 포인터
topPtr = topPtr->next; //topPtr이 다음 노드를 가리킴
delete tempPtr; //노드 삭제
}
}
ItemType StackType::Top()
{
if(IsEmpty())
throw EmptyStack();
else
return topPtr->info; //탑 포인터가 가리키는 노드(현재 노드)에 저장된 데이터 값
}
bool StackType::IsFull() const
{
NodeType* location;
try {
location = new NopeType; //노드 생성 가능 여부 판단
delete location; //삭제
return false; //스택이 Full 하지 않음
}
catch(std::bad_alloc exception){
return true; //스택이 모두 차 있음
}
}
IsEmpty()도 IsFull()과 비슷하게 구현해주면 된다.
연결 리스트로 자료구조를 구현할 때 주의해야 할 점이 있는데, 바로 스택의 지역 변수가 메모리에서 사라지더라도, topPtr은 자동으로 해제되지 않는다는 것이다. 이 때 소멸자를 사용해 topPtr의 메모리 영역을 해제해줘야 한다.
StackType::~StackType(){
NodeType* tempPtr;
while(topPtr != NULL){
tempPtr =topPtr;
topPtr = topPtr->next;
delete tempPtr;
}
}

Leave a comment